The rolling circumference of the wheels is determined and stored by the navigation system during the wheel calibration procedure.
Important!
Wheel calibration must be carried out when one or both front wheels have been changed.
The following faults can occur if a system has not been calibrated or has been calibrated incorrectly.
Wheel calibration can be carried out following two different methods:
As a rule, "calibration by measurement" should be carried out. When implemented correctly, only this method guarantees exact recording of the tyre rolling circumference.
The "specification of tyre size" method assumes the aid of the vehicle owner who, after entering the value, must correct (precision adjustment) it over a longer period of time.
Both methods are described in the following.
Workshop calibration
This method makes it possible to precisely determine the tyre rolling circumference.
The following aids are required for the wheel calibration procedure:
Important!
First carry out sensor test and diagnosis for wheel calibration based on a customer complaint.
Preparation

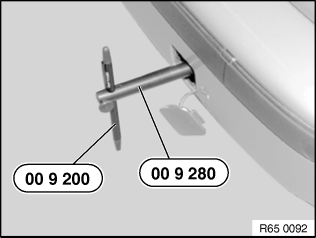
Unclip cover for towing eye at rear. Fit special tool 00 9 280 in the towing eye and fit the telescopic rod 00 9 200 in the hole of the special tool and clamp firmly.
Calibration procedure
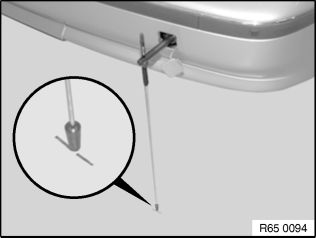
1st step
Lock vehicle in position with handbrake! Extend telescopic rod and mark the starting point on the ground with a felt marker.
2nd step
Switch on ignition in vehicle and select calibration menu on the on-board monitor. The menu is selected as follows:
An information page appears on the on-board monitor and the calibration menu after "continue".
3rd step
Enter "Start" on the monitor and drive straight ahead for 6 to 8 m at dead slow speed (greater than 1 km/h). Pay attention to the following points:
Apply brakes after approx. 6 to 8 m, immediately apply the handbrake and take out of gear. Enter "Stop" on the on-board monitor.
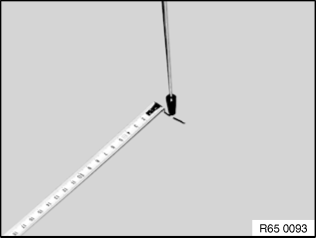
4th step
Mark end point with felt marker and measure the driven distance between the start mark and end mark with a tape measure to an accuracy of 1 cm.
Enter the measured distance on the on-board monitor.
5th step
After entering this distance, a straight ahead distance of approx. 100 m must be driven. Avoid moving the steering!
A note is indicated if the driven distance was too short or if the steering was moved too much.
Wheel calibration is completed after driving this distance and can be concluded with "End calibration".
Important!
Common mistakes in the wheel calibration procedure are:
Note!
When braking and driving off, for a short time the vehicle speed is below the minimum speed of approx. 1 km/h necessary for the wheel sensors. The vehicle then covers a distance which is not recorded by the navigation system.
It is therefore absolutely necessary that the measurement distance is covered quickly and without braking.
After calibration, the calculated calibration value (pulses per revolution) can be displayed and printed out on the BMW DIS.
Output takes place via "Service functions" - "Read calibration data of speed sensors (wheel sensors)"
The value does not change while driving the vehicle.
In the event of customer complaints, the print-out can serve the workshop as proof that the customer himself/herself has changed the calibration value.
Customer calibration
This method offers the technically experienced customer who frequently changes the wheels/tyres himself/herself the option of carrying out the wheel calibration himself/herself.
The rolling circumferences stored in the system for the individual types of tyres, however, are only nominal values which refer to standard specifications.
Additional fine adjustment is necessary due to the fact that, in many cases, the actual rolling circumference of the wheels mounted on the vehicle deviate from these values.
The procedure described in the following is only possible with the vehicle stationary.
The calibration value can be corrected if the specified metre data deviate continuously when subsequently driving with the navigation system.
Once again observe the indicated metre reading with regard to regular deviations.
Note
Due to the fact that the data in the stored map material is not "accurate to the metre" the indicated distance data always deviates to a certain extent from the actual distance. The data must therefore be observed over a longer period of time before and after fine adjustment in order to be able to determine whether the accuracy improved or deteriorated after adjustment.
The calibration data of the workshop calibration are overwritten by the customer calibration.
Please inform the vehicle customer accordingly!